Chemists have assigned voltage potentials to different chemical species according to their propensity to accept electrons. These voltage potentials are called “standard reduction potentials”. Table 1 contains a list of standard reduction potentials. Here the reduction potentials for different species can be compared under standard conditions of concentration, pressure and temperature.
Their values are calculated relative to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE), which has been assigned an arbitrary potential of 0,00 mV (marked in green). The strongest reducing agents have the highest negative potentials, and the strongest oxidizing agents have the highest positive potentials.
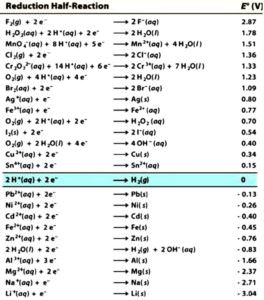
The table lists reduction potentials under standard conditions, but ORP meters are used to measure the potential of water under non-standard conditions.
In our discussion of voltage potential above, we recall that we described a potential difference between two points, the measured point (water sample) and one
Reference point (reference electrode).
This potential, expressed in millivolts, is called the “redox potential” (or ORP) and is a measurement of the electrical potential energy produced by a pair of species in water. One is in oxidized form and the other in reduced form, each in a specific concentration.
The name given to this pair of oxidized and reduced species is redox couple. A redox couple consists of either a strong reducing agent and a weak oxidizing agent or a strong oxidizing agent and a weak reducing agent.
As their dissolved concentrations change, the redox potential of the water also changes.
The ORP reading and whether it is positive or negative depends on which redox couple we are talking about and the relative concentrations of each species in the redox couple. A positive ORP indicates that the water has a tendency to act as an oxidizing agent, while a negative ORP indicates that the water has a tendency to act as a reducing agent.
Hydrogen water can also be called H2 water, hydrogen-rich water, hydrogen infusion water, or hydrogen-enriched water.
Excerpt from the book by Randy Sharpe: “The relationship between dissolved H2, pH and redox potential”




