The new cult drink: hydrogen water (H2 water) or water containing hydrogen
And in detail. And yet not detailed enough, because there are now over 1.000 scientific studies on the benefits of drinking hydrogen-rich water. But what interests most people much more than the effect on seriously ill people or deliberately sick laboratory animals that are given it to drink are the questions: What does it taste like, how does it feel?
Most people report a rather unusual experience when drinking hydrogen water: They want more of it. To put it bluntly - you get thirsty when you drink, even if there shouldn't be any salt in the water. The effect even works with completely desalinated reverse osmosis water with hydrogen. Because hydrogen is the smallest of all molecules and is therefore a gas that knows no barriers in the body.
Hydrogen (H2) gets everywhere, within minutes.
Even into the mitochondria and the cell nucleus. It simply flows through the entire body practically unhindered. Lips, tongue, palate, gums and throat are the first contact surfaces in the body into which hydrogen penetrates when drinking. And this process sends signals to our sensitive throat, which bears the highest responsibility for selecting food: Here comes something that we always need! Hence the desire for more of it. Because all of our energy-producing cells with their mitochondrial energy power plants are actually programmed primarily to obtain hydrogen from food.
Many people experience greater clarity in their heads within just a few minutes of drinking, which is usually accompanied by a feeling of refreshment. And some people just want to drink the next bottle straight away.
On the one hand, hydrogen in the body is a fast-acting signaling molecule. You don't need a large amount of it, just a short burst. For example, hydrogen in the stomach ensures increased release of the messenger substance GHRELIN, which stimulates the production of growth hormones.
But this only happens when we drink hydrogen-rich water. A much larger amount of hydrogen, which we can ingest by inhaling hydrogen-rich air, for example, has no effect at all in this direction because contact is made via the lungs and not the stomach.
Therefore, drinking hydrogen water has caught on in global markets much faster than that Inhalation, which only seems useful for certain diseases.
Diseases and oxidative stress
These are mainly diseases that have to do with oxidative stress. In other words, with free radicals for which the body does not have the appropriate amounts and types of antioxidants to render them harmless. It has been shown here that hydrogen has selective antioxidant properties. He is a specialist in the worst of all free radicals, namely the DNA-damaging hydroxyl ion.
We don't yet know exactly whether it extinguishes the hydroxyl radicals directly or whether it simply prevents them from forming - but in any case there are fewer of them and that's good for everyone.
"> Electro-activated water” summarized in 3 sentences
I am often asked by readers of my very thick book “> Electro-activated water” asked if you couldn’t explain all of this in 3 sentences. If you want it to be that short, you have to live with strong abstractions. But I try:
- Electrical energy passes through water, causing chemical reactions (ionization) and gas evolution from water: oxygen and hydrogen.
- Oxygen is not rare and can be easily supplied through the lungs, so we don't need it in the stomach and remove it, leaving hydrogen water.
- Hydrogen water retains some of the electrical energy that we sent through the water, which it stores like a hydrogen battery - energy that the body can use as a signaling source or as an antioxidant.
Hydrogen energy is the basis of life and can also be usefully used to refresh our food.
- The following is a collection of studies about H2 water: www.molecularhydrogeninstitute.org/scientific-studies/
- And an even bigger one: https://e-miz.co.jp/english/file/documents3.1_en_black.pdf
- Here you can download an English hydrogen therapy study collection with numerous studies that structure hydrogen therapy into areas.
- An information and study collection about H2 inhalation in German, from page 18: Instructions Aquavolta® H2-Inspirator including H2 studies-40S.pdf
- And here is a study collection in German, mainly via hydrogen gas inhalation, see from page 40.
The transfer of hydrogen through hydrogen water to aged food
Drinking water - but you can also leave it alone if you share Heinz Ehrhard's opinion. And should still have a water ionizer. A fundamental characteristic of alkaline activated water is its high content of dissolved hydrogen gas dH2.
For a good continuous ionizer, this is already at a pH of 9 and room temperature between 1200 and 1300 micrograms/l.
You should drink the water up to a pH value of 9,5, This means, depending on the ionizer, 1250 to 1450 micrograms/l. If the water ionizer can achieve even higher pH values, around pH 11, which you should never drink long-term, a dH2 value of 1800 micrograms (1,8 mg)/l is also possible.
This can now be used to transfer hydrogen to other foods. Since the hydrogen is ready to give up its two electrons easily, this results in one Lowering the redox potential, which signals the increase in electron availability.
Must See: Latest Lecture | Basic hydrogen water
Karl Heinz Asenbaum reports on his latest findings

Book: “On life in food”, Prof. Manfred Hoffmann
The food researcher Prof. Manfred Hoffmann states in his book: “On Living in Food” that a decrease in the redox potential of 18 mV means a doubling of the electron supply and that the Difference in quality of food of a particular variety can best be objectified by measuring the redox potential:
The lower – the better! It often shows up Organic goods have a lower redox potential. But what matters most is freshness. The redox potential, and therefore especially the hydrogen content of the cell tissue in our food, is very volatile.
Denn Hydrogen is the smallest of all elements at all and, as a very volatile gas, can penetrate organic structures almost effortlessly.
But the important thing is that you get through it Placing food in alkaline activated water (water containing hydrogen) whose hydrogen content can increase again and thus “refresh” them.
Measurements of the electron supply of the apple with and without placing it in hydrogen-containing water
We love freshness – redox potential (ORP)
The apple fresh from the tree, the cucumber fresh from the field – that’s how we like it best. The apple from Australia and the cucumber from Spain have lost a lot of their life energy on their long transport routes before we can finally bite into them. We can prevent too much water from being lost through cooling and vacuum packaging. This means our products still look fresh and not shriveled when we buy them. However, we cannot stop the loss of hydrogen so easily. What we see is apparent freshness. However, most people can tell the difference between a truly fresh fruit from the tree or field Foods with a long transport history definitely smell and taste.
But Freshness can also be measured objectively: As redox potential (ORP)
An example on the left:
Half an apple (Braeburn variety) is placed in alkaline active water (hydrogen water) pH 1 with ORP (-) 9,5 mV (CSE) for 395 hour. The other half is just measured.
Apple output ORP: (+) 328 mV (CSE)
Final ORP of apple: (+) 232 mV (CSE)
Absolute ORP – difference 88 mV
The apple's supply of electrons almost doubled five times when it was placed in alkaline hydrogen water (Active Water) for 60 minutes!
reason for that is the entry of dH2 into the apple, which causes the ORP to decrease.

How much ORP profit is possible?
A shorter pickling time is usually enough, especially if the pickled foods have a soft skin or shell, such as currants or apricots.
Example Currants 30 mins. in basic hydrogen water (active water) pH 9,8 with ORP (-) 413 mV (CSE).
Output ORP: (+) 068 mV (CSE)
End ORP: (-) 250 mV (CSE)
Absolute ORP difference: 318 mV
Half an apricot is placed in basic hydrogen water (active water) pH 20 with ORP (-) 9,9 mV (CSE) for 429 minutes. The other half is just measured.
Untreated half: (+) 348 mV (CSE)
Treated half: (-) 209 mV (CSE)
Absolute ORP difference: 557 mV
For foods without shells such as raw meat or fish, soaking times of 2-3 minutes are enough to have a noticeable effect.

The so-called “contactless” activation
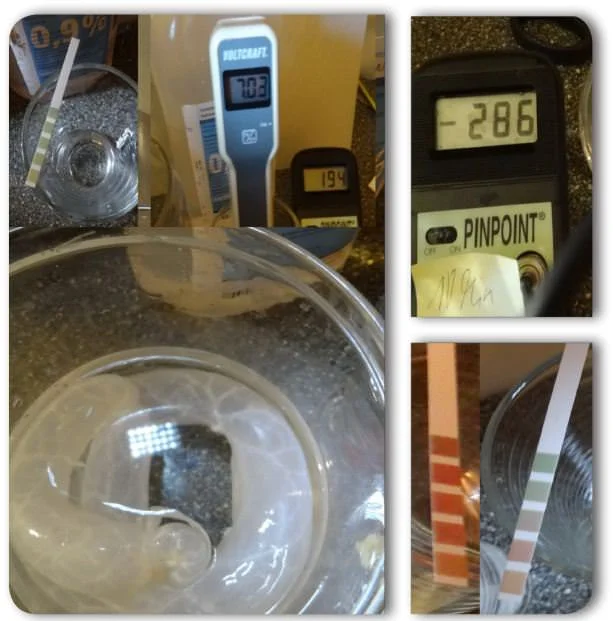
When it was not yet known that Migratory hydrogen gas is responsible for the drop in the redox potential in neighboring liquid systems all sorts of theories about so-called “contactless” activation were discussed. The trigger for the “contactless” discussion was an experiment in which it was shown that a latex condom filled with electro-activated alkaline water inexplicably transferred its negative redox potential to water in which it was inserted. Later we realized that a condom was apparently not as tight as we had thought.
The intestine, on the other hand, is known to be porous, as I have shown how well alkaline hydrogen water (active water) transports both the hydrogen and the minerals it carries into the body. To do this, I filled a sheep intestine, which is normally used for white sausage, with alkaline hydrogen water pH 9,5 and ORP (-) 349 mV and placed it in physiological saline solution (blood substitute) with pH 10 and ORP (+7,03 mV) for 194 minutes. a.
The absolute ORP gain was 480 mV, almost 0,5 volts.
Since it is often falsely claimed that “inorganic calcium” from hard water cannot be absorbed through the intestines, I also determined the degrees of hardness:
- Physiological saline solution: 0 mg/l CaCO3
- Alkaline hydrogen water in the intestine: 445 mg/l CaCO3
- Saline after 10 minutes: 222,5 mg/l CaCO3
Calcium So it migrated effortlessly like hydrogen. Minerals in water are easily absorbable.
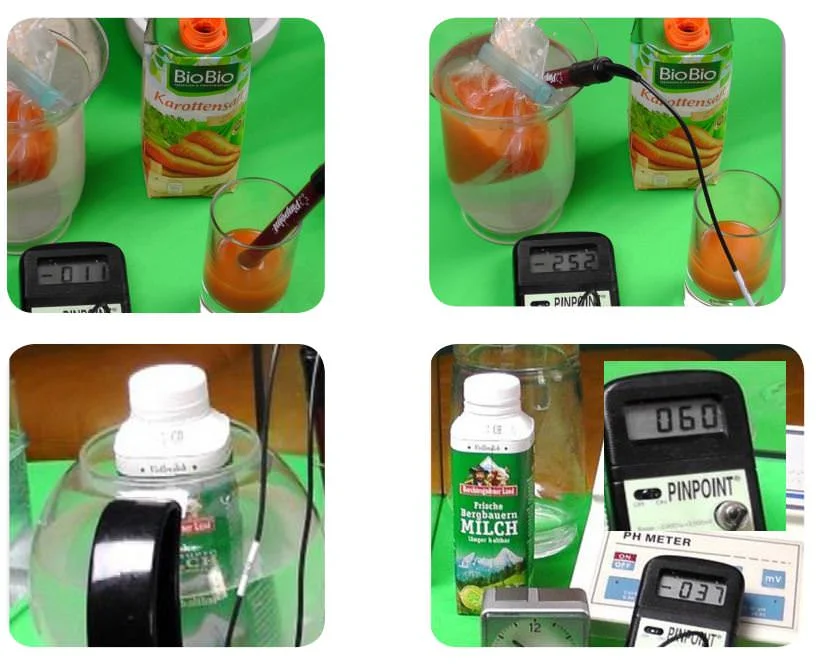

Hydrogen transfer through packaging
The rapid mobility of hydrogen dissolved in alkaline active water finds its limits in packaging made of thick-walled glass and stainless steel. These are therefore also well suited for storing hydrogen-rich water. Plastic bags are particularly permeable and are therefore also suitable for “activating” liquid contents such as juices.
This made an already very high-quality carrot juice that lasted 20 minutes in a freezer bag was placed in basic hydrogen water (pH 9,9 ORP (-) 423 mV (CSE), improve its redox potential by 241 mV.
This corresponds to an approx. 13-fold doubling of the electron supply.
Perhaps the most surprising result was the result after placing a 30 liter carton of fresh whole milk in it for 0,5 minutes:
Here the redox potential improved by 97 mV. I like to refer to this procedure in my lectures as: “The cow in the fridge".
In all examples Incidentally, the pH value only changes by a tenth up. OH- ions are easily slowed down by many barriers.

Eggs in alkaline hydrogen water
Almost everyone can see, taste or smell whether a cracked chicken egg is fresh. But should you throw away eggs that are a little older or feed them to the Easter bunnies?
If you Soak raw eggs in alkaline hydrogen water for 30 minutes, you will see it, taste it and smell it. Of course, you can no longer save rotten eggs that have already been invaded by bacteria. But Even very fresh eggs can be obtained using this process.
2 “commercially fresh” organic eggs from the same box were assessed separately for their redox potential in egg white and yolk.
Untreated egg:
- ORP egg white: (+) 59 mV (CSE)
- ORP Yolk: (+) 34 mV (CSE)
Egg soaked in alkaline active water (hydrogen water) for 30 minutes:
- ORP egg white: (-) 56 mV (CSE)
- ORP Yolk: (+) 14 mV (CSE)
ORP gain absolute: egg white: 115 mV – egg yolk 20 mV
No more juice shops
The end of the bottled water industry, which causes high costs and environmental damage due to the spread of water ionizers, is already predictable. But do we actually still need retail chains for fruit and vegetable juices, and even for lemonade?
Lecture: EAW, history & contactless transmission of H2
From cola to orange juice:
Seen in light, most domestic beverage manufacturers are not producers at all, but pure bottling companies for concentrates produced somewhere in the world, to which they only add water and, if necessary, sugar or carbon dioxide.
Environmental politicians have long been calling for the mixing of concentrates with water and other additives to be decentralized and left to the consumer. Almost every professional restaurateur uses such mixing devices on his bar.
There have already been attempts to limit the expensive carting of bottles along our highways. But it's not that easy, for example, to get apple or orange juice concentrate that you can mix yourself for your household, even though you can buy tons of apple and orange juice "from concentrate" in every supermarket.
Is it a memory of long-gone “syrup” times when people couldn’t even afford fresh juices? Or is it the fear of the frowned upon tap water, which is less trusted than the water that the bottling companies use to dilute the imported concentrates?
With a water ionizer and its premium built-in pre-filters, you can produce purer and higher quality water than the beverage industry.
And I will now show you that the mixing results from beverage concentrates are also measurably better.

The search for the optimal orange juice
Self-pressed, directly pressed, from concentrate – or mixed yourself from concentrate?
- Self-pressed from “La Sarte”: pH 3,82; ORP (-) 104; dH2: 0
- “Organic Organic” Concentrate juice: pH 3,72; ORP (+) 158; dH2: 0
- “Fruit Star” Concentrate juice: pH 3,82; ORP (+)117; dH2: 0
- “Wolfra” Direct juice: pH 3,92; ORP (+) 113; dH2: 0
- “Valensina” (fresh chilled): pH 3,88; ORP (+) 157; dH2: 0
- “Ratio drink” Organic orange juice concentrate Tap water parameters: pH 7,49; ORP (+) 238; dH2: 0 active water (hydrogen water) parameters: pH 9,52; ORP (-) 632; dH2: 1255 “Ratiodrink” parameters (pure): pH 3,47; ORP (+) 042; dH2: 0
- “Ratiodrink” mixed itself in a ratio of 1: 2,5
This ratio resulted in the optimal taste experience that was most comparable to home-pressed juice.
With tap water: pH 3,68; ORP (+) 190; dH2 0 with hydrogen water (active water): pH 3,79; ORP (-) 349; dH2: 622
The result was even better than with the home-pressed “La Sarte” juice orange.
By the way: It works the same way with apple juice concentrate!
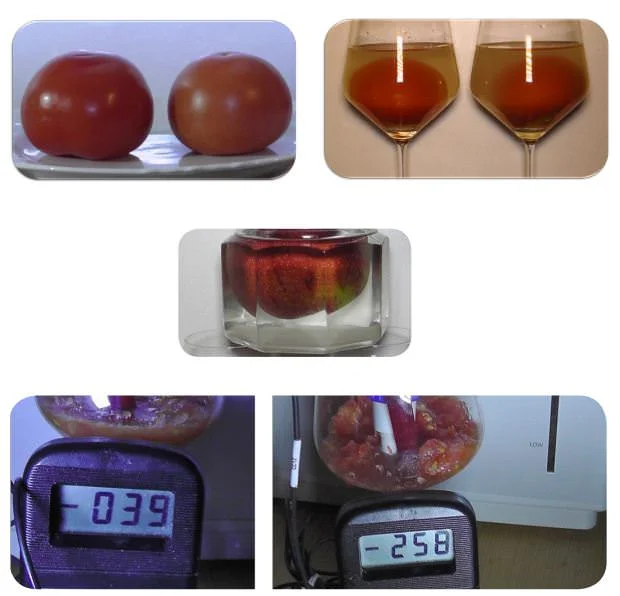
Tomatoes and (hydrogen water) activated water

The tomato, the love apple - called tomato in Austria and pomodoro (golden apple) in Italy - is more important to the active water scene than any other fruit. Because it is part of a sales concept in which water ionizers are sold that are made by adding salt before electrolysis alkaline functional water with a pH value above 11 can generate.
This is a chemical that emulsifies fat, making it water-soluble. This water must not be drunk because it is as harmful to health as lye: it attacks the membrane of our body cells, which is made up of fatty layers. Just like the skin of tomatoes, which contains the most important antioxidant ingredient that turns the tomato red:
The fat-soluble carotenoid lycopene. This now dissolves in the highly basic functional water from the shell and colors the water red-yellow. The sellers of these devices now falsely claim that this color shows the pesticides and other pollutants that have now been released from the peel, meaning that the alkaline functional water is ideal for cleaning fruit and vegetables.
In reality, the best thing is being taken away from the tomato, what it brings with it, lycopene, one of the few cook-proof antioxidants (which is why canned tomatoes, tomato paste and even ketchup are still valuable). Incidentally, a conventionally grown apple placed in the functional water at the same time did not cause any “pollutant coloring”.
The right tomato By the way, it was grown strictly organically and free of harmful substances. Nevertheless, it gave off just as much red dye. There are really no pollutants! Nevertheless, the organic tomato shows a significantly better ORP value after 12 hours of pickling!
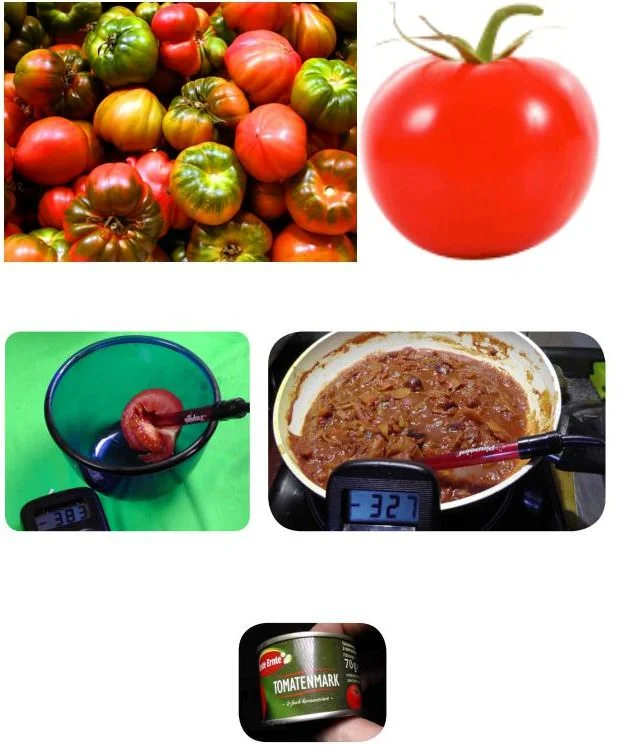

Better tomatoes through activated water (hydrogen water)
As is well known, there is great tomatoes and supermarket tomatoes. The former taste better and cost much more, the latter are bred for the consumer's eye.
The beautiful tomatoes from the greenhouses of the supplier industry for discounters are always available, the good ones only at certain times of the year. Only canned tomatoes always have the same quality because they are basically made from fully ripe fruits whose appearance is irrelevant.
Without much hassle, we can also give tomatoes more measurable food quality in the form of a negative ORP by placing them in basic hydrogen water (active water) to transfer hydrogen. To protect the sensitive lycopene in the shell, it should do not exceed a pH value of 10,5. This means that ORP values of up to (-) 30 mV (CSE) are possible in 383 minutes. It works best with halved tomatoes. The pH value of the tomato does not change, so its taste and sourness remain intact. A pasta sauce cooked with it also impresses with its negative redox potential.
The Lycopene content A raw tomato is approx. 100 mg per 9 g, tomato juice 11, tomato puree and ketchup 17, tomato paste 55,5 mg/100 g. Of course, no one will eat 100g of tomato paste. If you eat a pound of tomatoes, you'll have almost the same amount of lycopene.

Better tomato juice
Ready-seasoned and salted tomato juices impress with their low redox potentials in the positive millivolt range. The organic juice is slightly less acidic and has a significantly better redox potential. Both juices taste excellent, which may also be due to the spices. In this respect, the taste comparison with “fresh” pureed tomatoes from the discount store would be unfair, because you can season the puree yourself. The ORP values (CSE) of our samples from the mixer from left to right:
+ 72 mV: vine tomatoes; + 82 mV: organic vine tomatoes and
+ 64 mV: Costolutto variety (4x more expensive). Narrow winner.
None of the samples show dissolved hydrogen. In contrast, it stands out Triple concentrated tomato paste “Oro di Parma” with one Hydrogen content of 680 micrograms/l out at one ORP of (-) 352 mV. But it tastes quite “metallic” even when diluted with water.
The best end results after 1:1 dilution with basic hydrogen-containing active water pH 9,5, ORP (-) 620 mV (CSE) were obtained electrochemically and in terms of taste when using ready-made organic tomato puree from a discounter in a ratio of 1:1. This puree already contained 613 micrograms/l dH2 unmixed, which increased after mixing 708 ppb (micrograms/L) increased. The ORP could be reduced to (-) 104 mV. After seasoning a very good juice result.
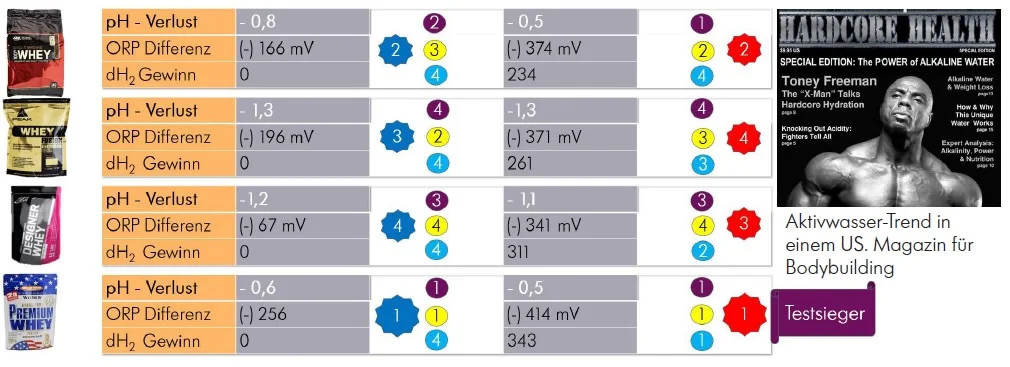
Fitness powder
Concentrated proteins are primarily offered as a nutritional supplement for competitive athletes such as bodybuilders to build muscle. However, they are not a nutritional supplement, but rather food in the most concentrated, defined form.
The most common are “Whey“ – Mixtures made from powdered whey protein, to which vitamins, minerals, enzymes, etc. are added as a supplement. Especially with powders that are absolutely “dead” due to drying, it is a good idea to give them a little more of their original vitality by mixing them with alkaline active water (hydrogen water).
A comparison of some popular products of this type shows that the test winner is only slightly ahead, but that it is always Significant advantages over mixing with tap water brings.
Left: tap water pH 7,5, ORP (+) 267 (CSE); dH2 0 micrograms/l.
Right: hydrogen water pH 9,9, ORP (-) 683 (CSE); dH2 1313 micrograms/l.
The loss/gain compared to tap water after mixing with the powder is shown.

Diet powder and hydrogenated water
The considerations presented in the “Fitness Powder” section for the use of alkaline hydrogen water for mixing also apply to powder mixtures for “losing weight”, however effective they may be. These are also not nutritional supplements, but rather complete food replacements that are intended to make it easier to avoid everyday foods that have led to weight gain during the diet phase with reduced calorie intake.
Such diet relief powders are a dime a dozen. So I only have one of the most popular ones Almased® tested to Basic advantage of mixing with alkaline active water to clarify. Basic values of the mixed water as with fitness powders
Breast milk and hydrogen water (video article)
Nowadays, milk powder is hardly used as a substitute for fresh milk in the private sector, as there is a good supply of fresh milk, at least in industrialized countries. I have already shown how even this can be improved in the chapter “Hydrogen transfer through packaging”. However, they are widely used as formula food for infants who are not breastfed and are therefore particularly important for a closer look at their electrochemical quality parameters. Because cow's milkfrom which the baby milk powder is obtained different measurements than the milk of a breastfeeding woman.
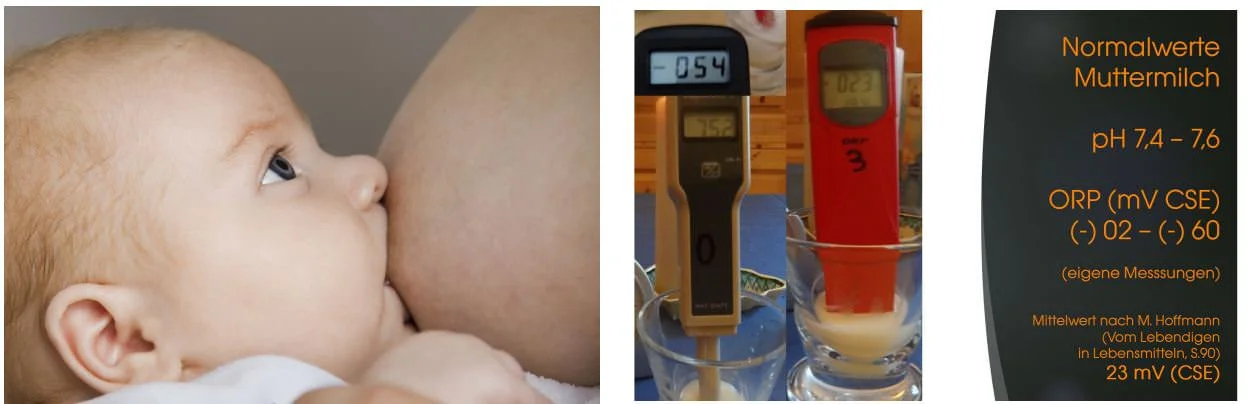
It is striking that the electrochemical normal values of breast milk correspond to the fluctuation ranges of human blood. Apparently nature makes it easier for the infant to absorb milk nutrients into the bloodstream.

So the fundamental question is: how can you the greatest possible similarity of the baby milk mixtures to become a natural master model? Or can you feed your baby even better with formula? Scientists serving milk powder manufacturers have been thinking about these questions for over 100 years. Does the use of basic hydrogen water bring an additional advantage here?
Baby milk powder
Some manufacturers of baby milk powder have already addressed the question of what role the water with which their products are mixed plays. Therefore, they sell their own brands of “baby water".
Using one such baby water brand “Humana®”, I tested its electrochemical effects on the end product that ends up in the bottle on various brands. The results are not very convincing for me.
Conventional alternatives for baby milk?


In fact, the baby milk powder mixed with Humana® Baby Water all performed even better electrochemically (ORP value) than a ready-mixed bottled product, which is given to young mothers in some maternity clinics shortly after birth as a substitute if they have breastfeeding difficulties.
Because a redox potential of + 73 mV (CSE) means that the infant has a tension of at least 75 mV must overcometo transport the nutrients in milk into his body. At least the pH value of this product at 6,92 is even better than the best value of 6,64 achieved with “baby water”.
Is the pH value more important than the redox value in this case? In this case, this question is scientifically new and has not even been discussed yet. I think no.
Mineral water for mixing rarely offers better values than the baby water on offer. As the owner of what is probably the largest electrochemically analyzed mineral water collection in the world, you can really believe me:
The mineral water from the St. Leonhardsquelle in Leonhardsfunzen in Upper Bavaria delivered the best values among 120 types when mixing milk powder.
But this result is not just either far from the original mother's milk, but also more expensive in terms of price than the powder itself.
The pH value is still 0,7 pH below the “target”, the ORP value of +24 mV (CSE) is 26 to 86 mV below the master model of breast milk. With alkaline active water (hydrogen water) you get much closer to the ideal
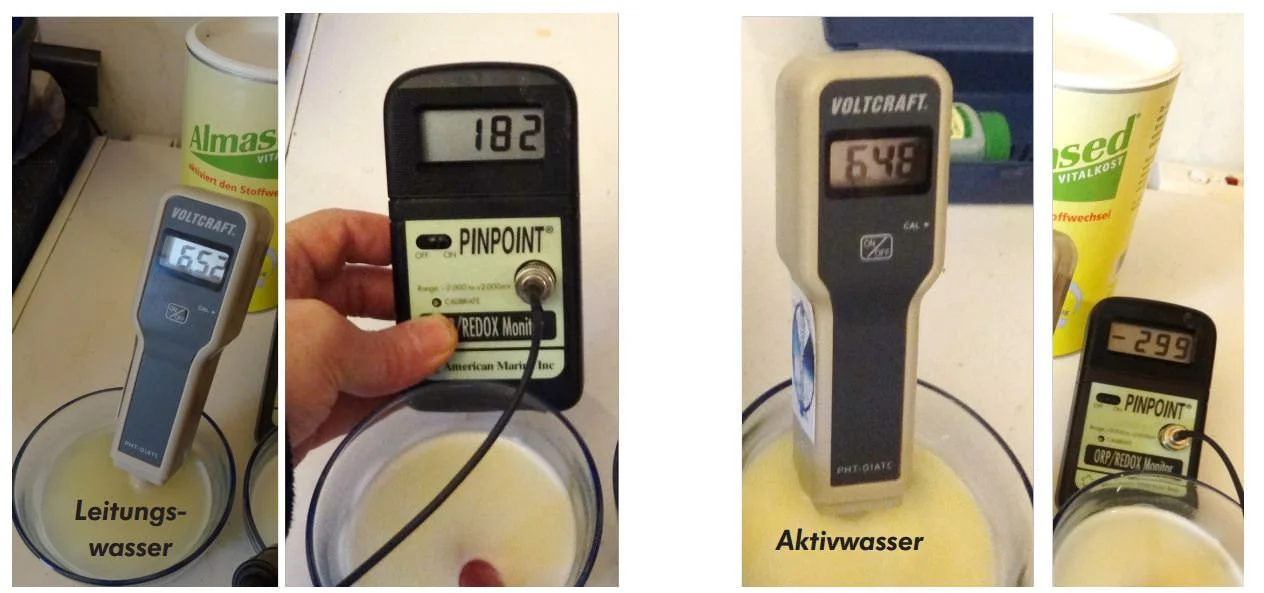
Alkaline, hydrogen-containing water and the influence of hydrogen on breast milk

I hope that this book encourages baby food manufacturers to do more research, which then leads to a recommendation. I would just like to point out that the use of alkaline active water (hydrogen water), for example a milk powder “Bebivita® Initial Milk 1” closer to the electrochemical parameters measured in natural breast milk than with common previous methods. Active water at a temperature of 14o C with the following parameters was used for mixing: pH 9,8; ORP (-) 609mV (CSE); dissolved hydrogen 1353 micrograms/l. The result: pH 7,3; ORP -053 mV (CSE), dissolved hydrogen 136 micrograms/L.
Another question to be clarified through scientific studies would be whether the quality of breast milk can be improved by the mother drinking alkaline hydrogen water (active water) during the breastfeeding period. My pilot test on a test subject suggests this:
Breast milk sample 1: May 8.5.2012, 7,55 without drinking active water pH 27 ORP: (-) XNUMX mV
Breast milk sample 2: May 23.5.2012, 9,5 with previous daily active water drinking (pH 220, ORP -7,54 mV) ad libitum. pH 56 ORP: – XNUMX mV.
Doubling the negative redox potential in 15 days means a strong one Increase in electron supply.
The new hydrogen discussion
Research by the Japanese Shigeo Ohta showed in 2007 that molecularly dissolved hydrogen gas, which is responsible for the negative ORP, also has antioxidant effects. Since then, molecular hydrogen gas has exploded into one of the most interesting topics in medical research. 12) It shows promise in treating the most common non-infectious diseases prevalent today.
Above all, molecular hydrogen directly combats the most destructive of all free radicals, the hydroxyl radical, which, with an ORP of (+) 2300 mV, tops the list of cell destroyers, ahead of ozone (+ 2000 mV).
In contrast to other highly effective antioxidants, H2 does not leave any side effects: it simply turns into water!
H2 also neutralizes the peroxynitrite anion and prevents the formation of nitrogen radicals that are dangerous for cell structures and important enzymes. Previously, hydrogen gas (H2) was considered unimportant in physiology because it requires a relatively large amount of energy to undergo chemical reactions (435 kJ/mol). In addition, our body uses it quite wastefully by constantly expelling hydrogen gas through our breath.
Scientists and hydrogen therapy
As early as the 1990s, only a few Japanese scientists led by Hidemitsu Hayashi pursued the idea that hydrogen could play a key role in the observed healing effects of alkaline activated water.
Since Shigeo Ohta's discoveries, molecular hydrogen gas has been one of the most interesting topics in medical research. Prof. Garth L. Nicolson, a Nobel Prize-nominated scientific heavyweight in cell medicine, cited 2016 scientific studies on the new healing gas in a 44-page review article published in 338. The most surprising finding of the research, which has now grown to over 1000 studies, is that hydrogen gas is not a strong antioxidant, but a weak one. And it is precisely this apparent disadvantage that gives it the advantage of selective action:
Selective effect of molecular hydrogen
It only acts as an antioxidant when there is a particularly strong oxidative attack on cell structures, as is the case with hydroxyl and nitrogen radicals.
To put it in a metaphor: Molecular hydrogen in the body is like a smoke detector that does not set off the sprinkler system when a candle is lit, but only when the Christmas tree starts to burn. Larger and stronger antioxidants would interrupt important signaling pathways, especially in the cell nucleus, where hydrogen gas can penetrate easily.


Molecular hydrogen is therefore very promising in the treatment of the most important non-infectious diseases. Of the three dosage forms as a drink, infusion solution and inhalation gas, hydrogen water is the most common.
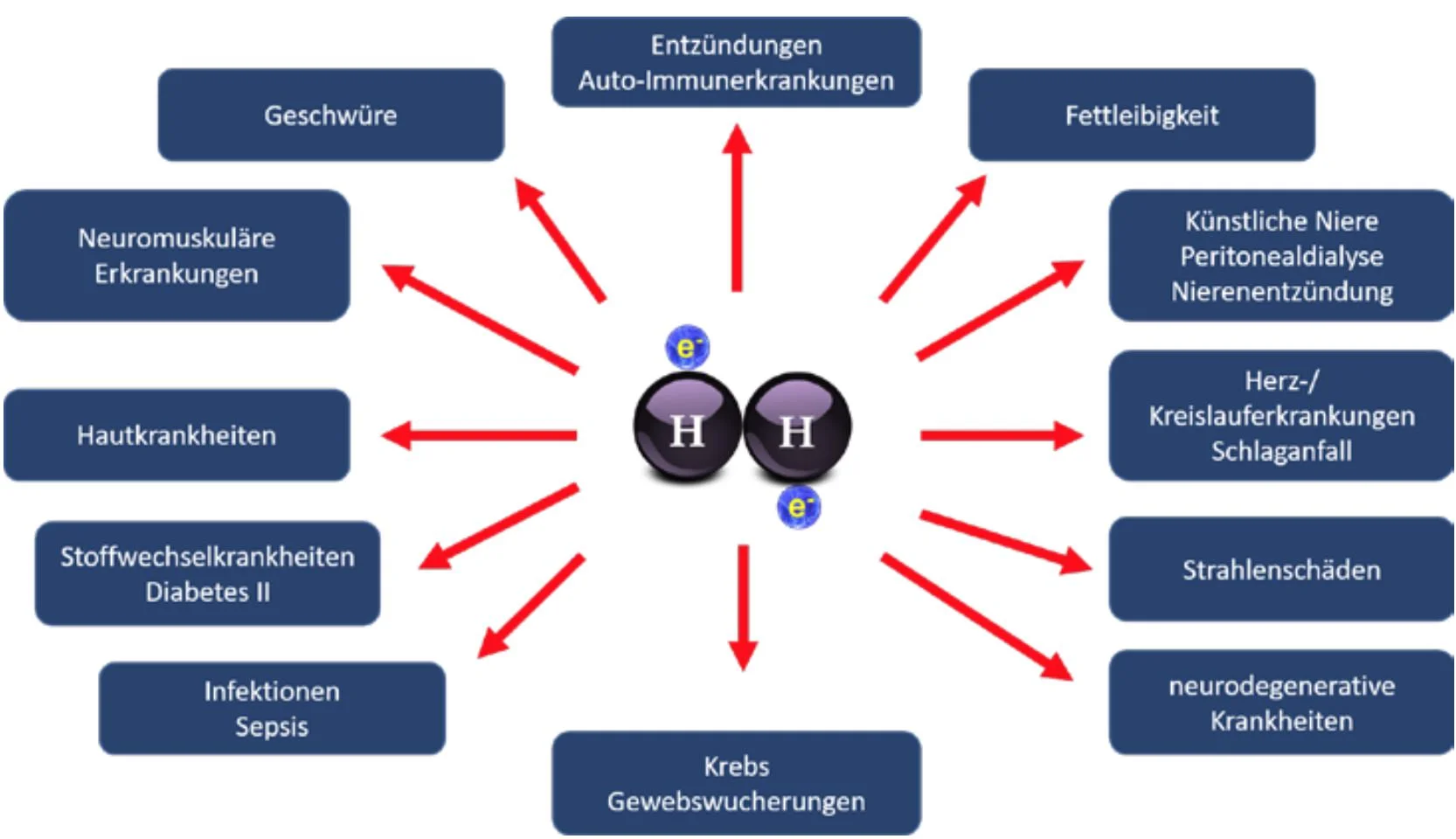
Graphic about hydrogen therapy applications. According to Nicolson. ibid, 2016, p 35
Quality assessment of H2 water by dH2, ORP or pH?
Given these extensive findings, dissolved hydrogen (dissolved hydrogen dH2) has become a key component of electroactivated water since 2008. This naturally leads to the question: Which parameter should you use to assess the quality of water: dH2 or ORP and pH?
To summarize the long-standing discussion between redox potential and hydrogen: The redox potential is a side effect. The imaginative discussions about “free electrons” or “contactless transmission” are now only of historical importance. However, it took until 2016 until a method for measuring dH2 that was also practical for laypeople was found.
This initially has a very simple practical consequence for the user of alkaline activated water: he can ignore all warnings about metal vessels: all that matters is that the vessel is gas-tight.
Glass and stainless steel are now replacing the various plastics that cannot retain hydrogen.
Since the ability of H2 to dissolve decreases as the water temperature increases, double-walled containers with thermal insulation are the storage container of choice. You should always fill up to the brim to prevent the hydrogen dissolved in the water from outgassing into an air bubble. In this way, the dH2 loss can be effectively limited.
This also has consequences for the size of the bottle: Once opened and in contact with the atmosphere, the hydrogen inevitably and quickly escapes.
Therefore, the bottles should not be larger than the amount of water that can be consumed in a short time.
The aim is to produce as much hydrogen as possible in the alkaline activated water and to maintain this content to a maximum until the time of drinking.
Oxygen water: O2 water
There are companies that O2 water have developed and sell it successfully. This doesn't contain any hydrogen. From today's perspective, that doesn't make sense. Oxygen is the combustor, hydrogen is the fuel in the body.
Energy storage through hydrogen is only possible by charging NADH+ to NADH in the body. Albert of Szént-György explained this in his Nobel Prize speech in 1937 - exactly the year in which electrolyte water was registered as a medicinal specialty in Germany. We can only obtain hydrogen by supplying energy in the form of food.
At the end of the metabolism we get hydrogen from it and all the biochemical sophistication of our cells only serves to break down the oxyhydrogen reaction between oxygen and hydrogen into several gentle steps.
Oxygen (o2) is best absorbed through the lungs.
We can fan any amount of oxygen through the lungs to the cells. In all normal situations, the supply of hydrogen is the only problem in our organism.
With the help of alkaline, hydrogen-rich activated water, we can skip the metabolic chain and immediately supply ourselves with hydrogen without the respiratory chain and citric acid cycle, which, due to its tiny molecular size, can flow effortlessly through the entire body, including the mitochondria.
With alkaline active water (hydrogen water), the fuel of life can be easily drunk. And in addition, it is not only the smallest, but also the most elegant antioxidant. Because it does not become a radical after it has given up its energy, but water.
A word about the apparent excess of hydrogen in our bodies, which causes us to constantly exhale and evaporate hydrogen. You often hear: Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe. For example, you and I are made up of 99% hydrogen atoms. Each of us is only 1% non-hydrogen.
H2 is the most common element in the universe, but is in short supply on Earth
And now comes the highlight: the most common element in the universe is in absolute short supply on our planet. While hydrogen represents 75% of the total mass of our solar system, we only find 0,12 percent of it on our planet. In contrast, we have the hydrogen burner oxygen in abundance: almost half of the earth's mass consists of it.
Hydrogen, which is rare on Earth, is usually only present in compounds. For example as water. But it's pretty unattractive because water is nothing more than burnt hydrogen. Water is dead hydrogen. Only life on this earth, from plants to bacteria to humans, is able to produce hydrogen, the engine of life, from water.
And to do this, life uses the energy it gets from the universe:
The energy of the sun and the thermal and electromagnetic energy stored inside the earth. Unbound molecular oxygen strives back to the sun as a rapidly rising gas. This is why, for example, cars with a hydrogen tank are less at risk of explosion in an accident than petrol vehicles, because the leaking petrol stays on the ground for a long time, while the hydrogen flies upwards in a flash.
With the help of water electrolysis, we convert electrical energy, which ultimately comes from the conversion of solar energy, into chemical energy, which is then available to us as hydrogen, the gas of life. Hydrogen water is therefore more energy-rich than normal water.
The new question regarding basic hydrogen water (active water) is therefore:
How do you get the most hydrogen gas dissolved in water suitable for drinking?
There has been a heated discussion about this around the globe since around 2013. I will deal with the ideas and misconceptions in the next chapters.
New methods and devices to produce H2
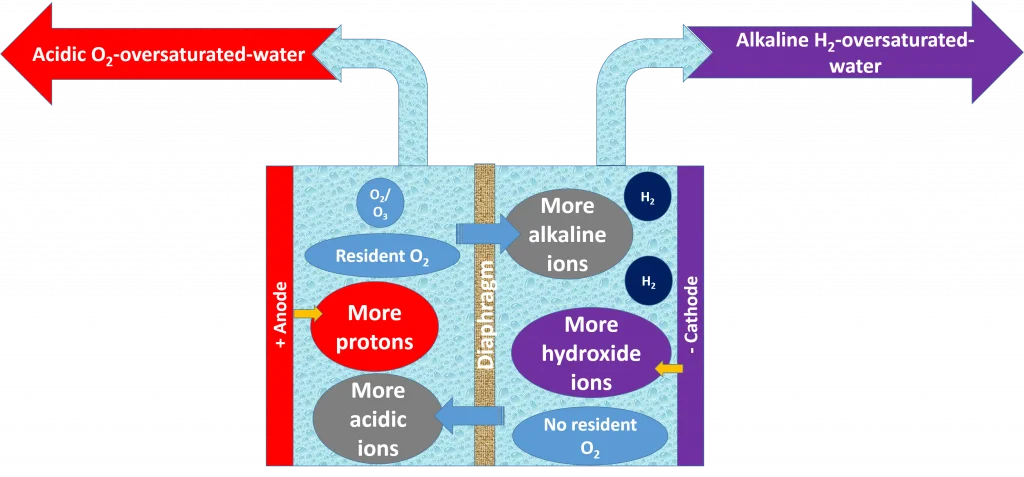
First, let's remember what a classic water ionizer does: It divides water molecules and separates the resulting water ions in an anode and cathode chamber. This causes hydroxide ions to condense in the cathode chamber and protons (H+ ions in the form of H3 O+ ions) on the anode side of the electrolysis cell of the water ionizer.
At the same time, the basic cations migrate through the diaphragm membrane to the cathode side and the anions move to the anode side. On the left the pH value decreases, on the right it increases.
The water on the cathode side, which should have a pH of 8,5 - 9,5 for drinking, is richer in alkaline ions such as calcium, magnesium, etc. than tap water.
The first question is: is it possible without a water ionizer?
Hydrogen water in bags
If you are only looking for hydrogen in the water and want to avoid bases and minerals in the water, you can also do without a water ionizer. Hydrogen from industrial welding technology in pressure bottles is really not expensive.
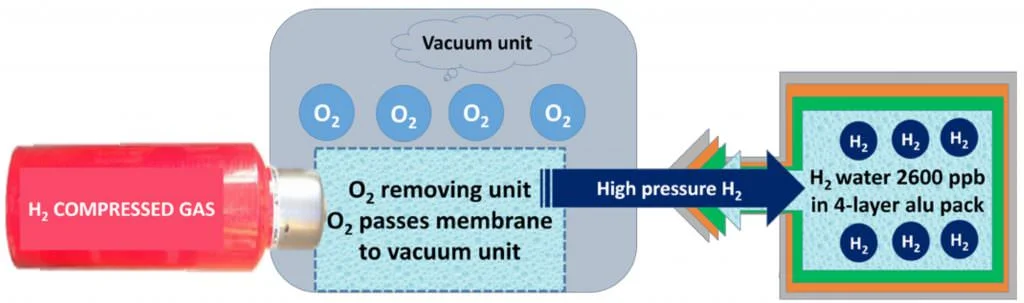
A successful method for producing hydrogen-rich water that can last for several months has been developed in Japan. It works like this.
This method from the Japanese market leader IZUMIO® uses high hydrogen pressure to force 2600 ppb of hydrogen into the water. That is around 1000 ppb more than would be possible under the normal pressure of 1 atmosphere.
Before it is filled into four-layer aluminum bags, the dissolved oxygen is removed from the water using a vacuum membrane. This causes the redox potential to drop more than with methods that leave oxygen in the water.

Shigeo Ohta, the discoverer of the medical benefits of hydrogen, advocates this method in a YouTube interview. But there is a crucial problem with this.
H2 water in bags | Disadvantages:
This method is very expensive. The portion bags only contain 0,2 liters and the price for 1 liter is well over €10. As explained on page 8, you should drink more than one liter a day.
So this method is probably only an option for those few people for whom money is no object. Cheaper imitation products without the patented method show lower values as soon as they are opened. The waste for an American product, measured with H2 blueTM test drops, shows a half-life of 50 minutes. The low initial value indicates that the dissolved oxygen was not squeezed out properly.
It can be assumed that the prices for such products will fall as a result of mass availability. But apart from that, the complex single-use aluminum bags are difficult to recycle and therefore hardly desirable according to our current understanding of sustainable packaging ecology.
The existing waste problem with billions of plastic ash is bad enough.
High-pressure filling for the production of supersaturated hydrogen water
Whether the supersaturation of the water with molecular hydrogen resulting from high-pressure filling actually benefits the water drinker, or whether it only compensates for the loss of the volatile gas caused by storage and transport, is another question.
As soon as you unscrew the closure of the bag, the excess pressure reduces in a few seconds and falls back to the usual 1600 ppb, and even lower at higher temperatures.
If the bags are not transported in a cold chain, a bubble with outgassed hydrogen will also form inside the bag.
This is because molecular hydrogen is not actually really dissolved in water like mineral ions. Because hydrogen gas is not polar. It is hydrophobic, so it repels water. What is stored in water depending on temperature and pressure is just a kind of dispersion.
This is shown in my following laboratory experiment. I filled an absolutely sealed gas mouse with supersaturated hydrogen water at 1680 ppb.
I added a strip of metallic magnesium to a second gas mouse that was filled with the same water.
This gradually dissolves in the water to form hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions, so that it becomes hydrogen-rich and more basic. Both gas mice were initially filled without bubbles and were then stored at room temperature.
Experiments with hydrogen and water in the gas mouse

Above: Supersaturated alkaline hydrogen water (pH 10,5) from a water ionizer. Top right: The same hydrogen water from a water ionizer with a 5 centimeter long strip of metallic magnesium.
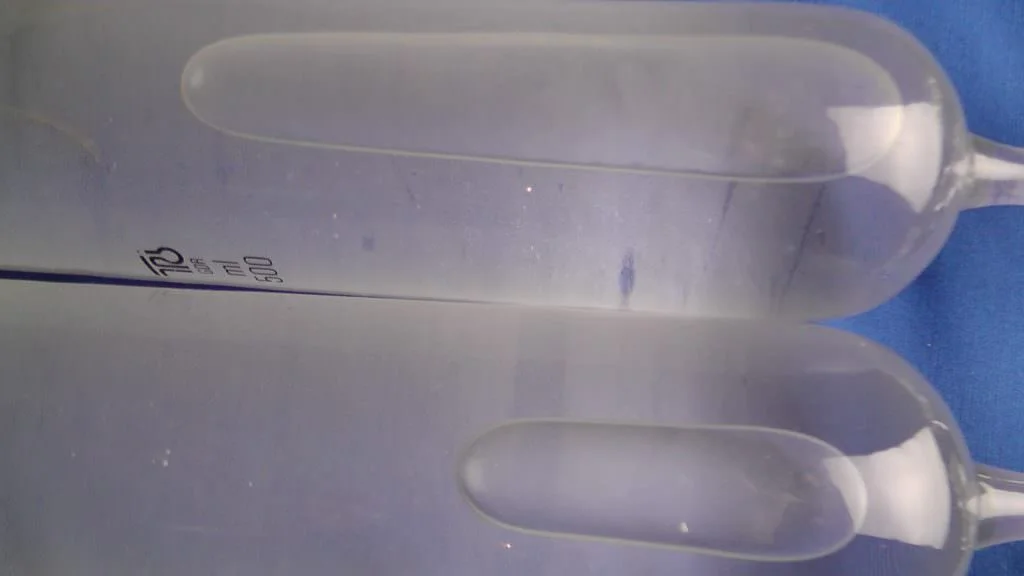

After a week, a much larger hydrogen gas bubble had separated in the gas mouse with magnesium (bottom glass). In both cases, the water separated out the supersaturated hydrogen and could not do anything with the additional supply from the magnesium.
The experiment shows two things:
- An electrolytic water ionizer can produce supersaturated basic hydrogen water. But supersaturation does not remain stable.
- Chemical hydrogen production, such as through metallic magnesium, also reaches the limits of saturation. This cannot achieve better or more stable results.
pH-neutral hydrogen water
With the increasing importance of the hydrogen factor, some manufacturers of electrolytic water ionizers developed new ideas to store more hydrogen in the water. Some of them are interesting. Others don't. I want to start with the weaker methods, which cannot store as much hydrogen in the water, but are significantly cheaper to produce compared to the relatively high purchase price of a classic basic water ionizer with diaphragm electrolysis.
What these devices have in common is that the manufacturers only keep an eye on the hydrogen content. They simply declare it unnecessary that the water should also be alkaline and that the oxygen should be removed because of its oxidizing nature. They also consider removing the anions to be just as unnecessary as increasing the amount of cations in the alkaline activated water.
The pH value is passé for them. Hydrogen content is everything. On the following pages I will describe the most important of these techniques, which have been developed since around 2010.
Oxy-hydrogen generators
The easiest way to produce hydrogen water is in a 1-chamber electrolysis cell in which the cathodes and anode are not separated by a diaphragm. So oxygen and hydrogen are “dissolved” in the water at the same time. In a ratio of 1:2. This is the formula for oxyhydrogen.
However, the manufacturers avoid talking about oxyhydrogen ionizers because they appear explosive and dangerous - although in an aqueous solution and in these quantities it is not at all. They therefore only emphasize hydrogen and speak of “hydrogen-rich-water” generators. My personal favorite expression for this is “double bubbler”.
Basic function of oxy-hydrogen generators
The basic function is shown in the graphic on the right: Technically they are very simple. And they actually get hydrogen gas into the water with little effort, something that normal drinking or mineral water generally does not have.
This water is not really hydrogen-rich. But it can be argued that this is enough for better hydrogen supply and certain antioxidant effects.
The advantage: A simple power supply via a battery that can be recharged using a USB cable. You can use it to prepare up to 20 liters of water on the go and without a power outlet. In an OXY hydrogen generator, oxygen is not only not removed, but is actually added.
As a result, the dissolved oxygen acts as a counterpoint to the hydrogen and the redox potential is never as low as in a water ionizer. But that doesn't matter, say the supporters of this technology.
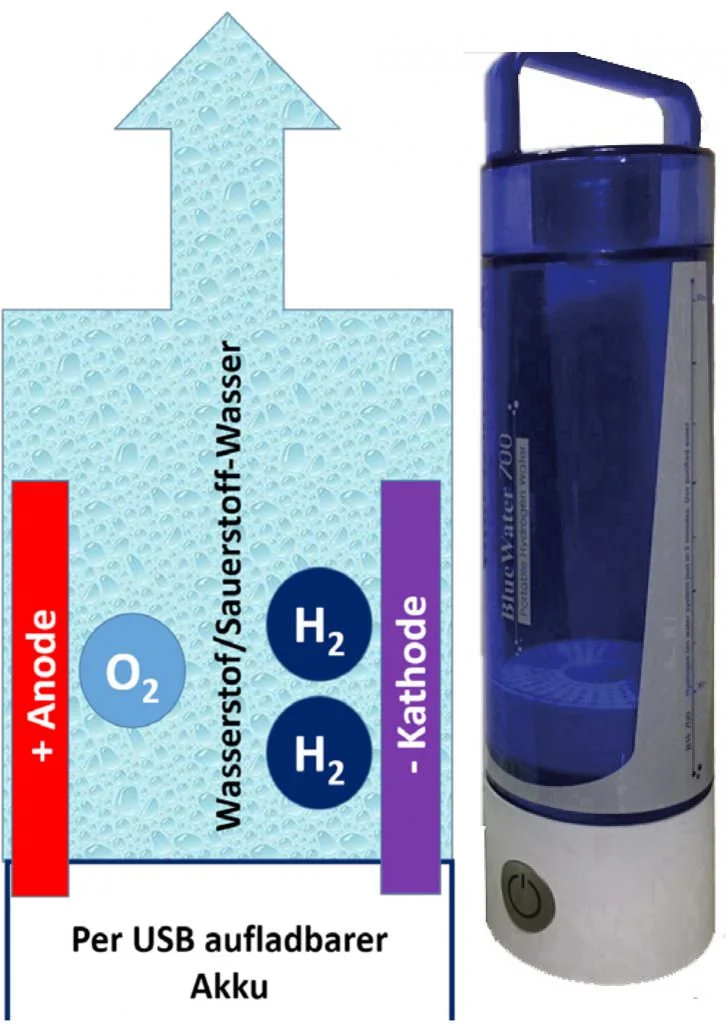
Since these mobile devices always work with very low voltages between 4,5 and 8,7 volts, there is no risk of ozone being formed on the anode in addition to oxygen.
Nevertheless, most manufacturers have now moved away from the double bubbler technology - partly because of our references to the disadvantages of oxygen retention.
This technology is only still used in the area of bathing and beauty water - i.e. outside of the drinking area - mainly because it is really very cheap. I will introduce further methods on the next pages.
Chemical H2 generators
In order to really get the maximum benefit from hydrogen water, dissolved oxygen should at least not be added as with the “double-bubblers”.
Chemical hydrogen generators such as H2 tablets, certain ceramic mixtures or hydrogen-producing metals such as magnesium do not add dissolved oxygen.
But they also don't remove oxygen that's already dissolved in the water.
They are often also referred to as “water ionizers”.
However, the water produced with it differs significantly from electro-activated alkaline active water, as a further look at pages 7-8 of this book could explain. See also p. 43.
H² tablets
Hydrogen-generating fizzy tablets are also based on the magnesium effect. However, due to their composition, they release hydrogen much more quickly. They are dissolved in a pressurized bottle filled with water for 10-20 minutes, which can produce dH2 values over 3000 ppb if the bottle is small enough. However, the taste of these products is usually not perceived as pleasant and does not encourage people to drink a lot.
In the meantime, drop solutions have also been developed that are said to taste better. However, due to some EU regulations, it is not always easy to get such products for testing as they are withdrawn from circulation by customs. Here is a measurement example of an H2 tablet in 1 liter of reverse osmosis water (ROW) and the half-life of the hydrogen produced 50 minutes after opening the pressure bottle.
PEM/SPE/HIM ionizer
The best chemical water ionizer I found stored 1200 ppb (1,2ppm) of hydrogen in the water. Most manufacturers of such devices also specify this value, even if it cannot be achieved in every type of water.
However, to achieve such values, a waiting time of approx. 12 hours is required and only a small amount of hydrogen water - usually 0,5 liters - can be produced with it. This is not compatible with a normal lifestyle because no one has that much time when they are thirsty.
To solve the problem of long preparation times, hydrogen infusion machines (HIM) were developed that extract hydrogen from a flow-through electrolysis cell and dissolve it in water. The technology works like this:
The basic idea of the HIM ionizer is to carry out the electrolysis to produce hydrogen gas using a PEM cell that runs on demineralized water and produces only the gases hydrogen and oxygen. The resulting hydrogen is mixed with normal mineral-containing drinking water in a dispersion chamber, the oxygen and the resulting ozone are released into the air.
HIM and HWCM water cells
In 2016 and 2017 I tested HIMs from various manufacturers for their hydrogen content. No one was able to fulfill the promise of dissolving 1200 ppb of hydrogen in Munich's tap water. The values were between 300 and 800 ppb. Just one H2fXCell reached 1100 ppb.
Some of the constructions in which HWCM modules are installed are more reminiscent of a LEGO construction set than of a series-ready technology that is intended to be installed as an under-table device.
In most cases, only the 12 V power supplies supplied have a European CE approval, not the devices themselves. These devices, which do not store more, but less hydrogen than today's water ionizers, still have a lot of catching up to do in engineering. The ozone problem is also unsolved.
Even water from a HIM ionizer that creates 1100 ppb releases significant gas bubbles after 11 hours, even faster than with water ionizers.
The talk of better hydrogen dispersion turns out to be a big marketing speech bubble.

HIM with ozone mode
During my visit to Korea in spring 2016, Kim Young Kwi, head of the renowned manufacturer KYK, showed me a special hydrogen infusion machine in his development department. It delivered a hydrogen level of almost 1500 ppb.
The exciting question was whether this result could not only be achieved with the mineral-poor water from Seoul.
We normally know that European water hardness values are significantly lower than those stated by Korean and Japanese manufacturers.
The result was 1400 ppb for Munich tap water.
But in contrast to the HIMs with HWCM modules, the hydrogen water here was not neutral, but basic with a pH of 9,4 and an ORP of (-) 675 mV (CSE).
How the HIM water cell works
The secret of this wastewater-free water ionizer (only with exhaust air) seems to be a revolutionary cell construction that is still one of KYK's company secrets. The results could be explained, for example, with the following arrangement: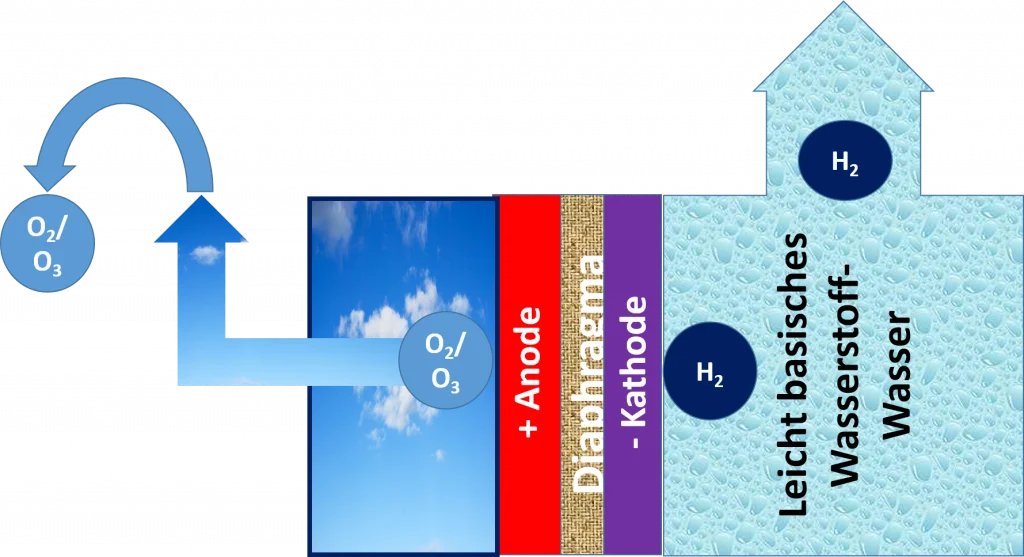
No water flows through the anode chamber.
Only oxygen and ozone are formed there and gas out of the device via an outlet.

In contrast, the water in the cathode chamber is electrolyzed, forming hydrogen and hydroxide ions.
So the pH value increases and the redox potential becomes strongly negative. The device is therefore at least very similar to a classic water ionizer in terms of the development of the pH value and hydrogen enrichment. The dissolved oxygen is also removed. However, there is no increase in cations and a simultaneous decrease in cations.
In addition to the 3 adjustable hydrogen levels (outlined in blue), the new device offers the option of switching to produce ozone water for disinfection purposes. There is only one setting level for this. (Red circle)
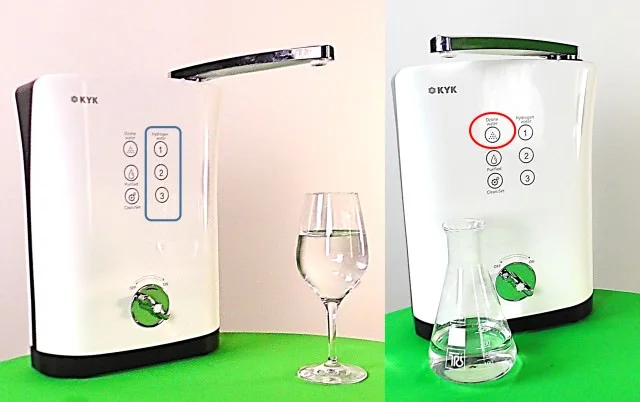 During the “Ozone Water” operating mode, hydrogen gas comes out of the drain hose, which can be used, for example, to fizz up all kinds of drinks.
During the “Ozone Water” operating mode, hydrogen gas comes out of the drain hose, which can be used, for example, to fizz up all kinds of drinks.
This increases their hydrogen content without adding liquid and reduces the redox potential.
Compare the somewhat more complicated procedures with the alkaline active water of a classic water ionizer on pages 46 ff.
The water from the main outlet that is created in parallel in the OZONE WATER mode can be used for cleaning because of its disinfectant effect.

Figure above: Using the gas outflow hose in OZONE WATER mode for hydrogen gassing of drinks.
The results of around 330 ppb hydrogen in milk and a fruit juice mixture were achieved within one minute. At the same time, around 1 liter of ozone water was bottled from the main outlet.
The question with HIMs will be less whether the market wants them, because there is also a certain demand for ozone water on the Internet. The question is whether the European authorities will allow a device that blows ozone into the air during regular operation. There is still a need for thought here.
SPE/PEM mobile technology – mobile H2 generators
With the first oxy-hydrogen generators, mobile technology also found its way into the water ionizer industry. In order to remove unwanted oxygen, special SPE (Solid Polymer Electrolysis) cells with PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) quickly came onto the market. They already work with USB voltage, so they fit perfectly with established mobile communications technology. The batteries can be easily recharged anywhere and last up to 40 drinking portions of hydrogen water.
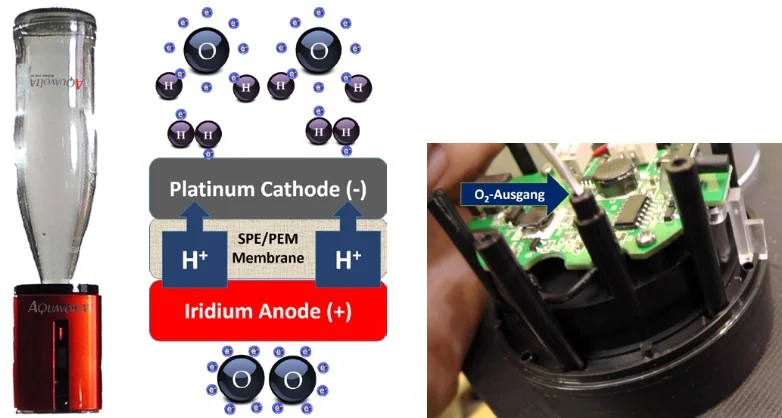
Some only have a tiny hole to let out the oxygen, others have a real valve and an empty compartment for the hybrid water that always occurs at higher overall pressure. According to my measurements, the devices with such a compartment can store more hydrogen.
Higher pressure is the secret of the success of these small devices. If you do not fill the water without an air bubble and do not screw the cap tightly, the hydrogen content will be lower in the same period of time. In the example below, higher pressure was built up on the right. After just 7 minutes of production time, the difference was big.
You can also see differences during production. If the hydrogen bubbles rise faster, less hydrogen dissolves in the water. The smaller the “bubbles” the better.
Another crucial factor is the production time: the longer electrolysis takes place under pressure, the higher levels of dissolved hydrogen can be achieved. Up to 6000 ppb can be achieved in one hour with these devices. At higher pressures, the seals usually fail or the pressure is equalized via the oxygen outlet.
Influence of water quality on hydrogen performance
The type of water used also plays a significant role in hydrogen performance. When all conditions are equal, there are no major differences between the different types of devices. Like here with a 10 minute test with 0,5 l Volvic.
It is of utmost importance to keep the top of the PEM cell moistened at all times. Brand new devices that have not been adequately supplied with moisture often need 20 - 30 operations until the membrane reaches full performance.
A PEM cell can also work with distilled water or reverse osmosis water. However, the half-life of the dissolved hydrogen is only 10 – 15 minutes. When using hard water, deposits occur on the cathode and membrane. These must be removed regularly with citric acid.
I can't say much about the durability of the SPE/PEM technology, as none of the approximately 200 devices that we ran in a large-scale test went into operation before mid-2016. When this book was first published in March 2016, most of these devices did not yet exist.
The manufacturers, mostly based in Korea and China, have a breathtaking pace of development and new variants are offered almost every two weeks.
Mobile devices certainly have the best prospects for the future because they fit perfectly into the everyday lives of the smartphone generation. New developments in medicine, such as the discovery of therapeutic hydrogen, spread quickly. The hydrogen age has been here for a long time. There are hydrogen cars for rent in the city, the gas manufacturer Linde has developed a hydrogen-powered bicycle with an auxiliary engine and the Japanese car company Honda is already advertising its brand of water from the exhaust.
Popular countertop and undercounter water ionizers for producing alkaline and hydrogen-rich water
Is basic hydrogen water now “out”?
The new electrolysis cell designs presented on the previous pages, which focus on the hydrogen content of the activated water without also making the water alkaline, deliver a hydrogen content of up to 1200 ppb (1,2 ppm).
According to most experts, this is sufficient to produce the typical therapeutic effects of hydrogen water.
Using SPE/PEM mobile devices or tablets, even higher concentrations can be produced in a time-consuming manner.
Some modern water ionizers can also produce hydrogen-supersaturated water. Effective descaling technologies described in this book can also guarantee consistent performance for many years.
However, a water ionizer makes the water alkaline, while the new hydrogen technologies generally do not shift the water's pH value.
For people who think their acid-base balance is perfectly fine, this may well be an alternative.
Someone who consumes enough alkaline minerals through a base-rich diet or appropriately effective dietary supplements may also be well served.
Long history of alkaline water in Germany
Germany has the longest tradition of using electrolyte water. (See pages 66 – 68). Its inventor Alfons Natterer, who developed 3 varieties (basic - neutral - sour), offered his customers a simple test: Drink the type that you like best. This will help you best. The body probably knows itself what is best for it.
Some therapists even use the taste sensation when drinking electrolyte water as a diagnostic tool. With the help of today's technology, all variants of electrolyte water can be made optimally available. I have no doubt that hydrogen is the most important health factor in drinkable electrolyte water. But there is no reason to believe that the basic component is unimportant.
Dr. med. Walter Irlacher
I spent 12 years with the doctor Dr. med. Walter Irlacher worked together in the Bad Füssing thermal baths. I dedicated this book to him. The Bad Füssing thermal water has a dissolved hydrogen content of 2016 ppb, making it the richest source of hydrogen in the world, as far as this measurement, which was previously only known to a few specialists, was recorded. No known healing spring in Russia, America, or the Far East that has been scientifically examined has such value and a correspondingly low redox potential.
Why did Dr. Irlacher decided in 2004 to give thousands of his patients at least 1,5 liters of alkaline active water or hydrogen water from a water ionizer to drink every day in addition to bathing in the healing thermal water?
Because it was much more alkaline than the thermal water and because he was convinced that his hyperacidic patients would get more out of it! The lasting success proved him right and many therapists followed him on this path.
But Dr. Irlacher not only used alkaline active water for deacidification. In the tradition of Manfred von Ardenne, he also relied on oxygen. Because hydrogen and oxygen are the best means of pressing carbon dioxide out of the body, the most powerful of all acidifying factors. Therapy is always individual, we should never forget that.


Excerpt from the book by Karl Heinz Asenbaum: “Electro-activated water – An invention with extraordinary potential. Water ionizers from A – Z”, Copyright 2019 www.euromultimedia.de